Glutaminyl Cyclase, Diseases, and Development of Glutaminyl
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
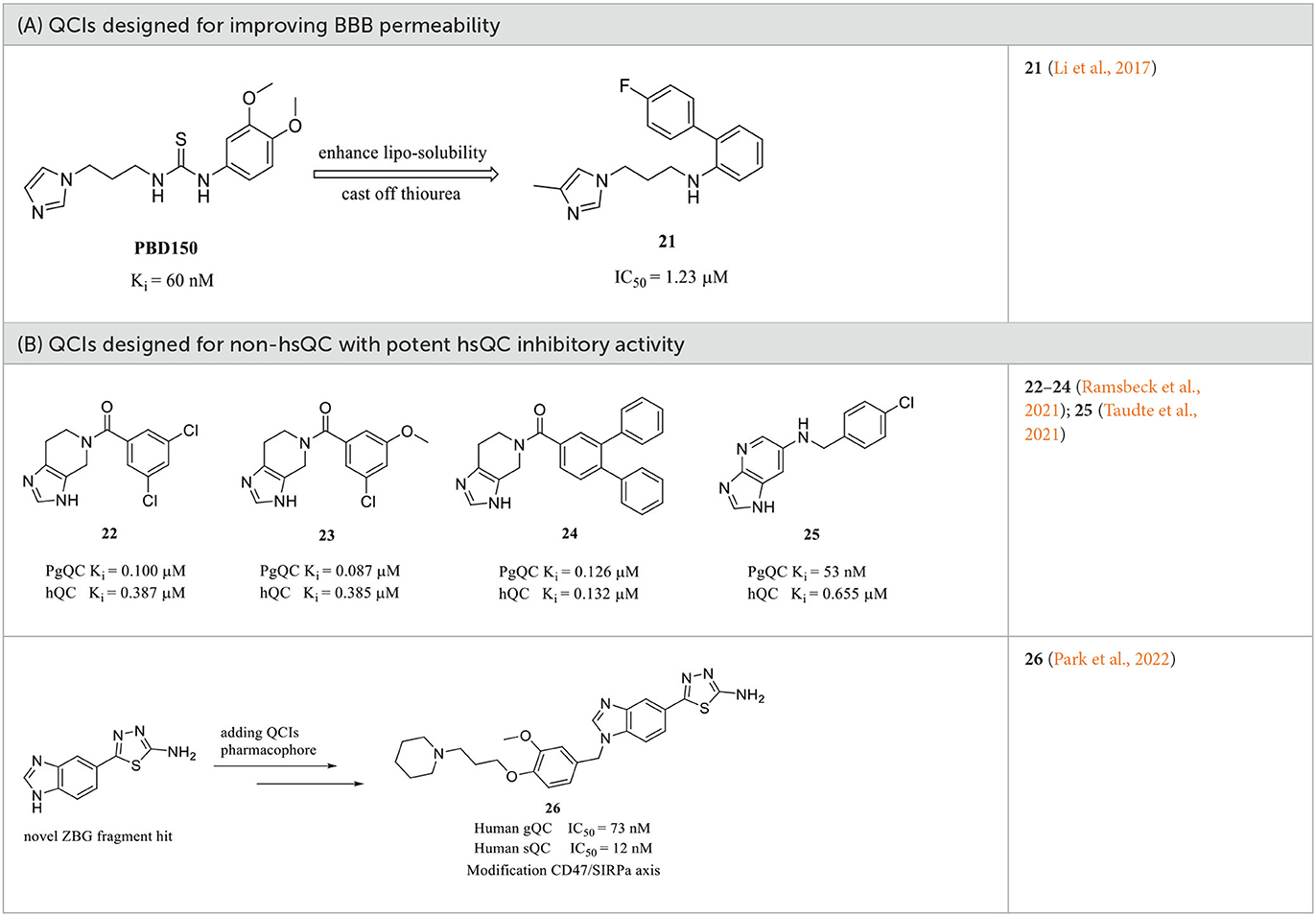
Frontiers Development and evolution of human glutaminyl cyclase inhibitors (QCIs): an alternative promising approach for disease-modifying treatment of Alzheimer's disease

Glutaminyl Cyclase, Diseases, and Development of Glutaminyl Cyclase Inhibitors

Therapeutic potential of glutaminyl cyclases: Current status and emerging trends - ScienceDirect

Upregulation of Glutaminyl Cyclase Contributes to ERS-Induced Apoptosis in PC12 Cells

IsoQC (QPCTL) knock-out mice suggest differential substrate conversion by glutaminyl cyclase isoenzymes

Glutaminyl Cyclase, Diseases, and Development of Glutaminyl Cyclase Inhibitors

Glutaminyl cyclase (QC) converts N-aminoterminal glutamate residue to
is a glutaminyl cyclase inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.5 μM.Glutaminyl Cyclase Inhibitor 1 is compound 23[1].[1]. Li M, et al. Synthesis and

Glutaminyl Cyclase Inhibitor 1

Crystal structures of human glutaminyl cyclase, an enzyme responsible for protein N-terminal pyroglutamate formation

Frontiers Development and evolution of human glutaminyl cyclase inhibitors (QCIs): an alternative promising approach for disease-modifying treatment of Alzheimer's disease
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







