Combination treatment of berberine and solid lipid curcumin particles increased cell death and inhibited PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway of human cultured glioblastoma cells more effectively than did individual treatments
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
The treatment of glioblastoma is challenging for the clinician, due to its chemotherapeutic resistance. Recent findings suggest that targeting glioblastoma using anti-cancer natural polyphenols is a promising strategy. In this context, curcumin and berberine have been shown to have potent anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effects against several malignancies. Due to the poor solubility and limited bioavailability, these compounds have limited efficacy for treating cancer. However, use of a formulation of curcumin with higher bioavailability or combining it with berberine as a co-treatment may be proving to be more efficacious against cancer. Recently, we demonstrated that solid lipid curcumin particles (SLCPs) provided more bioavailability and anti-cancer effects in cultured glioblastoma cells than did natural curcumin. Interestingly, a combination of curcumin and berberine has proven to be more effective in inhibiting growth and proliferation of cancer in the liver, breast, lung, bone and blood. However, the effect of combining these drugs for treating glioblastoma, especially with respect to its effect on activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways has not been studied. Therefore, we decided to assess the co-treatment effects of these drugs on two different glioblastoma cell lines (U-87MG and U-251MG) and neuroblastoma cell lines (SH-SY5Y) derived from human tissue. In this study, we compared single and combination (1:5) treatment of SLCP (20 μM) and berberine (100 μM) on measures of cell viability, cell death markers, levels of c-Myc and p53, along with biomarkers of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways after 24–48 h of incubation. We found that co-treatment of SLCP and berberine produced more glioblastoma cell death, more DNA fragmentation, and significantly decreased ATP levels and reduced mitochondrial membrane potential than did single treatments in both glioblastoma cells lines. In addition, we observed that co-treatment inhibited the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway more efficiently than their single treatments. Our study suggests that combination treatments of SLCP and berberine may be a promising strategy to reduce or prevent glioblastoma growth in comparison to individual treatments using either compound.

Curcumin Formulations for Better Bioavailability: What We Learned from Clinical Trials Thus Far?

Dose response curves of curcumin on neuroblastoma cell lines. Dose
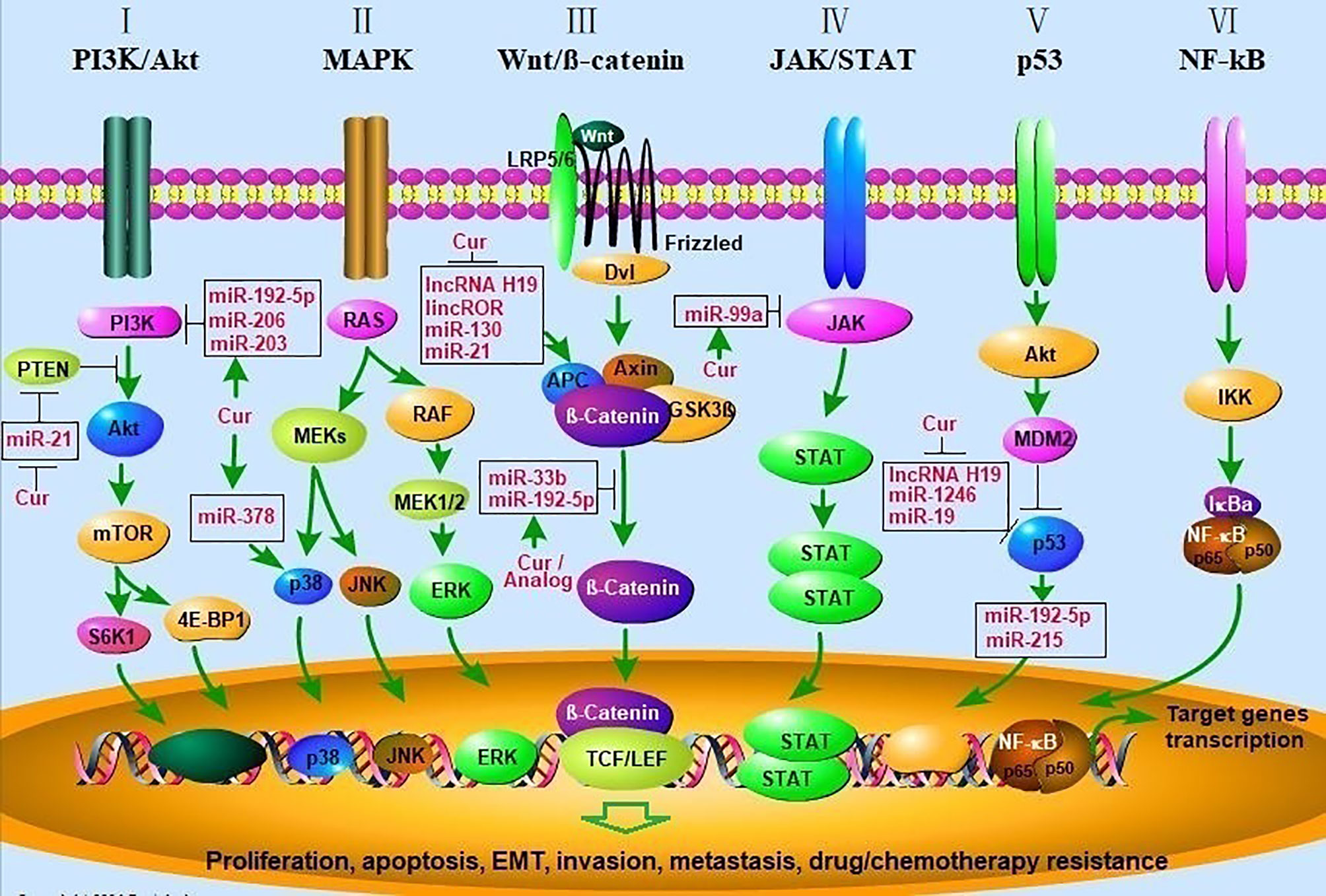
Frontiers Curcumin Regulates Cancer Progression: Focus on ncRNAs and Molecular Signaling Pathways
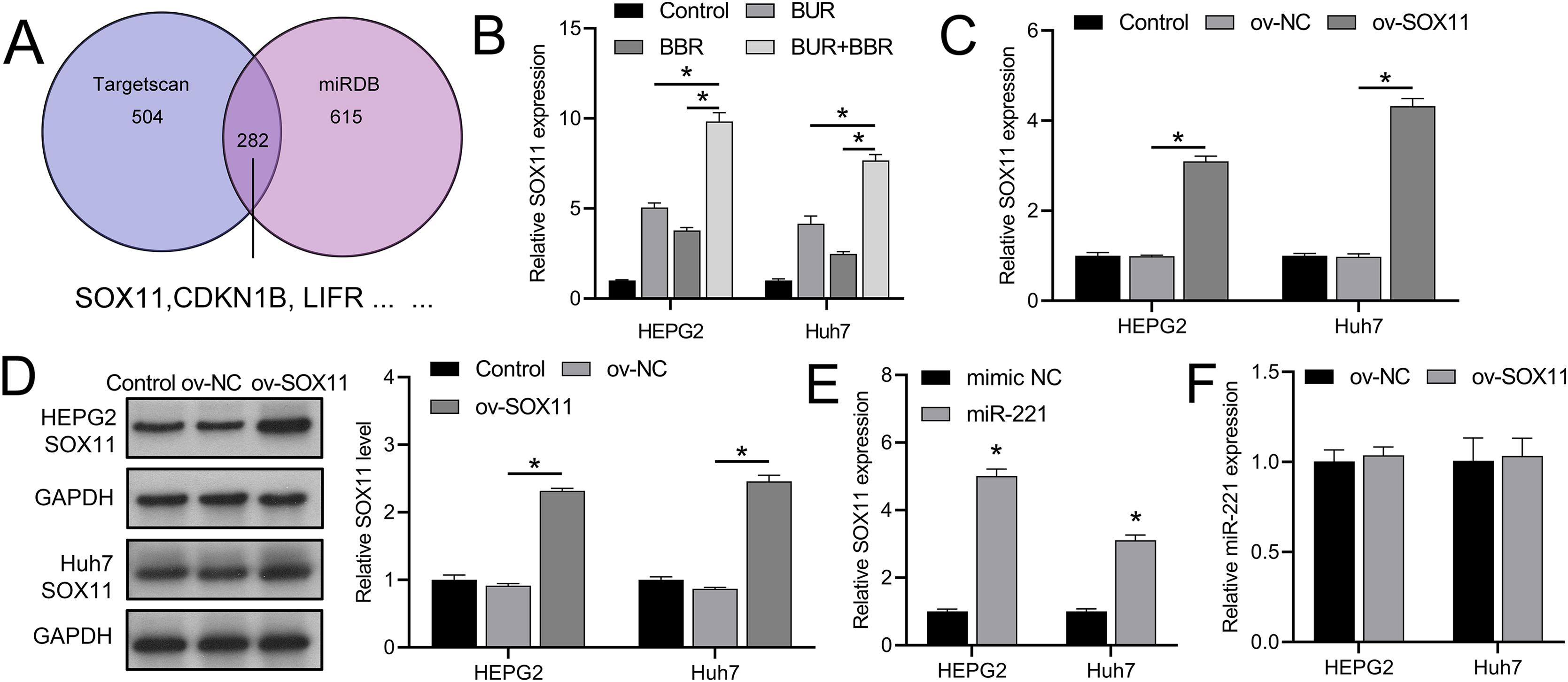
Inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma growth via modulation of the miR-221/SOX11 axis by curcumin and berberine [PeerJ]
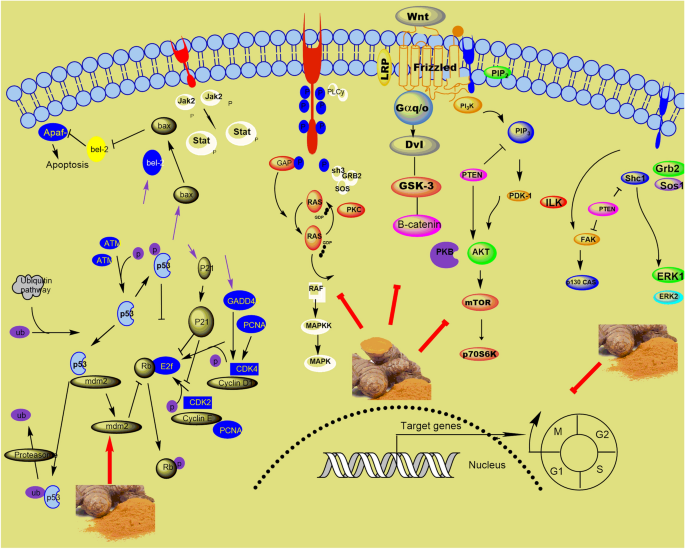
Review on the Therapeutic Potential of Curcumin and its Derivatives on Glioma Biology

BBR targets the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 pathway in GBM cells. A. Western blot

Recent advances in glioblastoma multiforme therapy: A focus on autophagy regulation - ScienceDirect
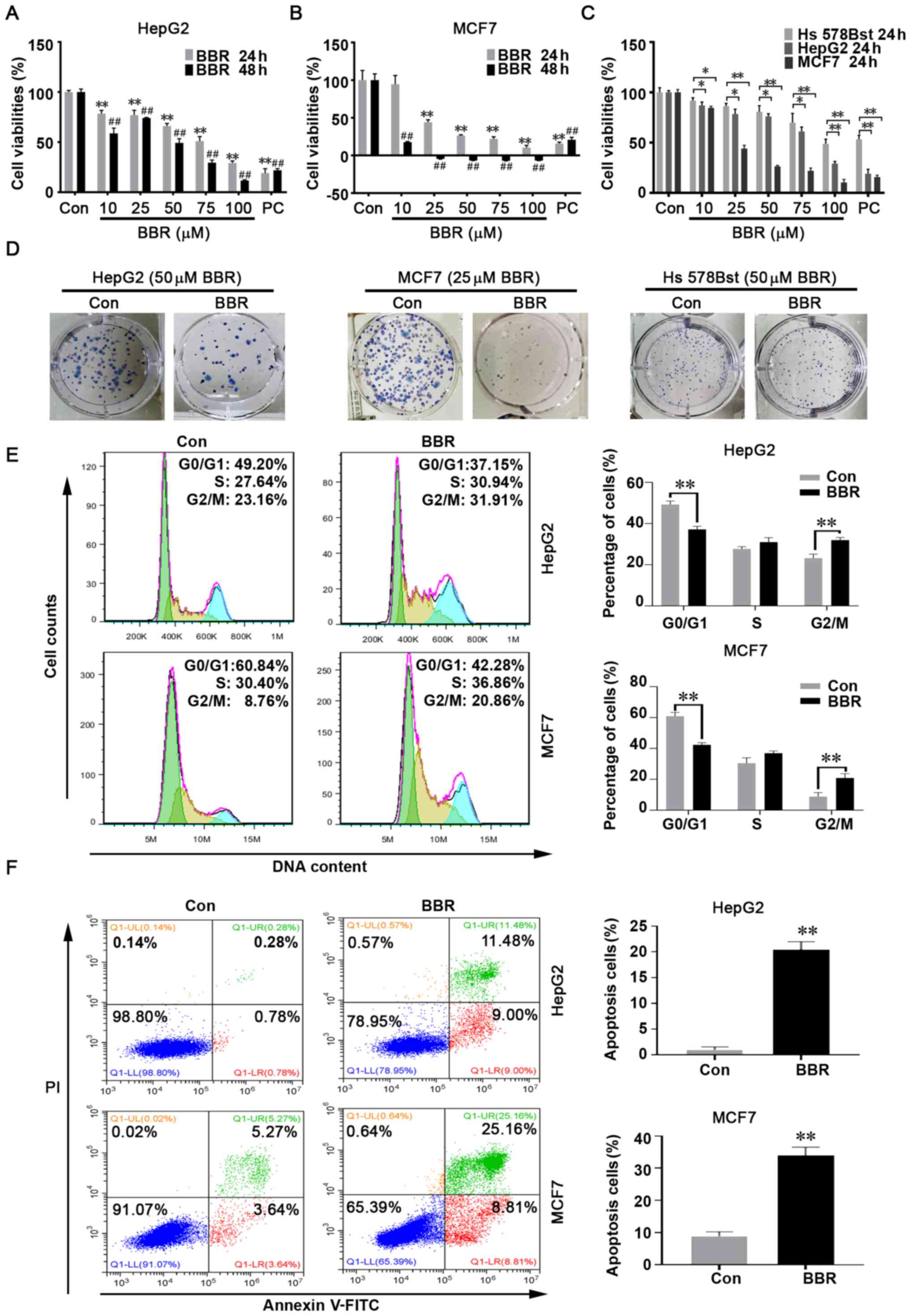
Berberine exerts its antineoplastic effects by reversing the Warburg effect via downregulation of the Akt/mTOR/GLUT1 signaling pathway

Curcumin potentiates the galbanic acid-induced anti-tumor effect in non-small cell lung cancer cells through inhibiting Akt/mTOR signaling pathway - ScienceDirect
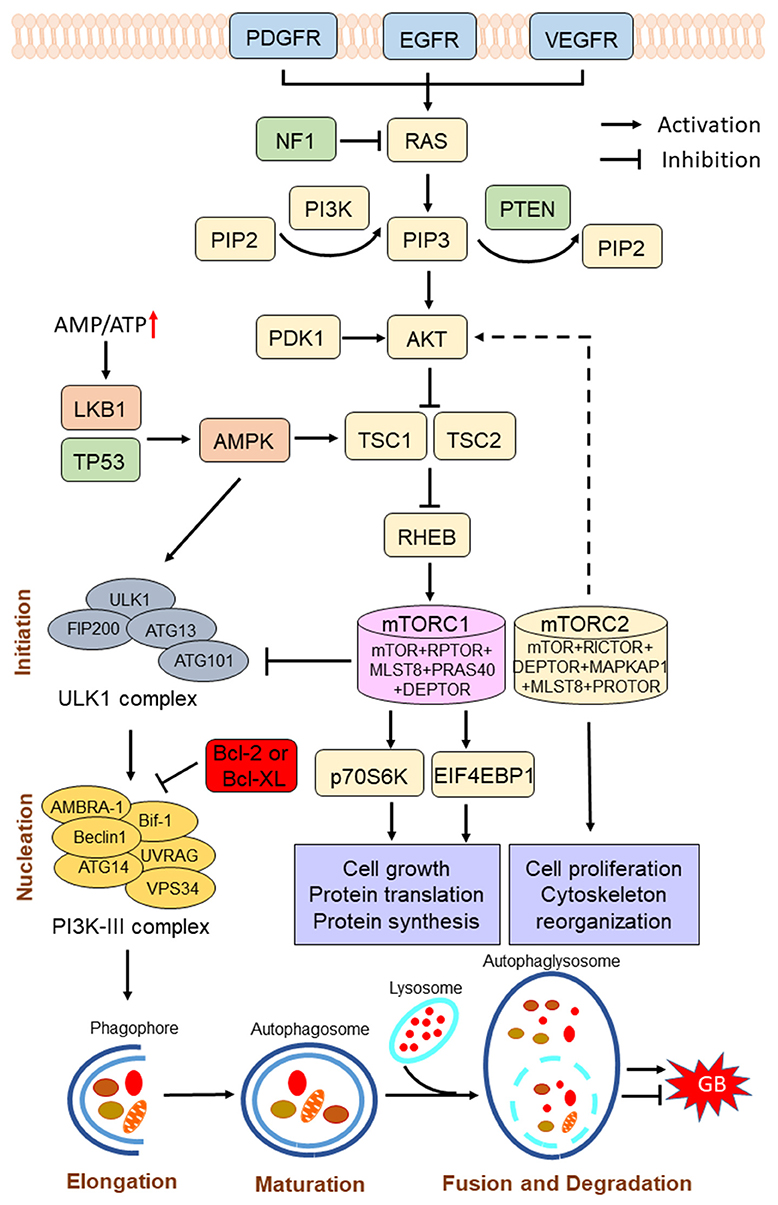
Frontiers Therapeutic Potential of Autophagy in Glioblastoma Treatment With Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signaling Pathway Inhibitors

Mixed Nanoscale Liposomes Co-Encapsulating Curcumin and Berberine Inhibit Activated Hepatic Stellate Cell-Induced Drug Resistance and Tumor Metastasis

PDF] Solid Lipid Curcumin Particles Induce More DNA Fragmentation and Cell Death in Cultured Human Glioblastoma Cells than Does Natural Curcumin
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)

/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_59edd422c0c84a879bd37670ae4f538a/internal_photos/bs/2023/t/D/ZOnIAZRO6j4jbJ44MXAw/whatsapp-image-2023-11-07-at-11.56.16.jpeg)




